Free
Food Safety Vs Food Defense
Description
|
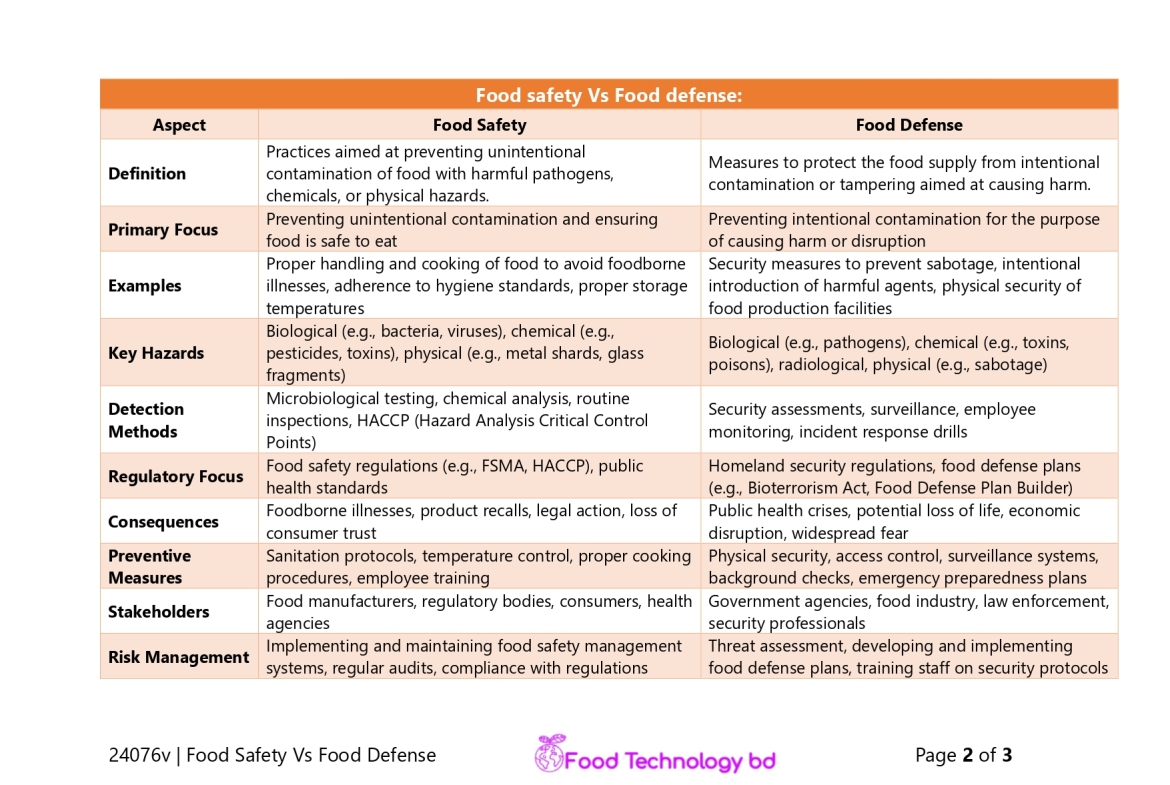
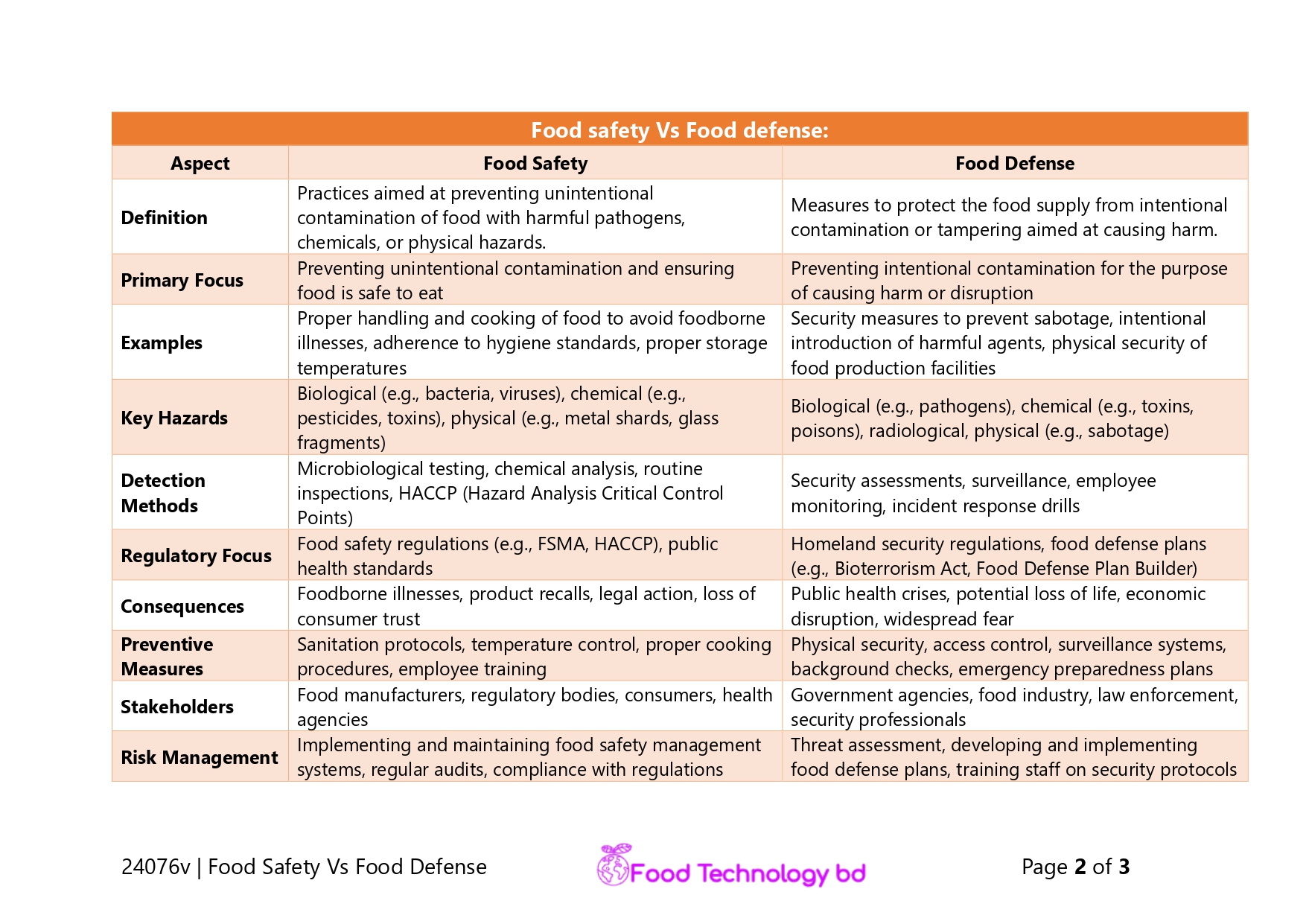
Food safety Vs Food defense |
||
| Aspect | Food Safety | Food Defense |
| Definition | Practices aimed at preventing unintentional contamination of food with harmful pathogens, chemicals, or physical hazards. | Measures to protect the food supply from intentional contamination or tampering aimed at causing harm. |
| Primary Focus | Preventing unintentional contamination and ensuring food is safe to eat | Preventing intentional contamination for the purpose of causing harm or disruption |
| Examples | Proper handling and cooking of food to avoid foodborne illnesses, adherence to hygiene standards, proper storage temperatures | Security measures to prevent sabotage, intentional introduction of harmful agents, physical security of food production facilities |
| Key Hazards | Biological (e.g., bacteria, viruses), chemical (e.g., pesticides, toxins), physical (e.g., metal shards, glass fragments) | Biological (e.g., pathogens), chemical (e.g., toxins, poisons), radiological, physical (e.g., sabotage) |
| Detection Methods | Microbiological testing, chemical analysis, routine inspections, HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Points) | Security assessments, surveillance, employee monitoring, incident response drills |
| Regulatory Focus | Food safety regulations (e.g., FSMA, HACCP), public health standards | Homeland security regulations, food defense plans (e.g., Bioterrorism Act, Food Defense Plan Builder) |
| Consequences | Foodborne illnesses, product recalls, legal action, loss of consumer trust | Public health crises, potential loss of life, economic disruption, widespread fear |
| Preventive Measures | Sanitation protocols, temperature control, proper cooking procedures, employee training | Physical security, access control, surveillance systems, background checks, emergency preparedness plans |
| Stakeholders | Food manufacturers, regulatory bodies, consumers, health agencies | Government agencies, food industry, law enforcement, security professionals |
| Risk Management | Implementing and maintaining food safety management systems, regular audits, compliance with regulations | Threat assessment, developing and implementing food defense plans, training staff on security protocols |